Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Eye Institute, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
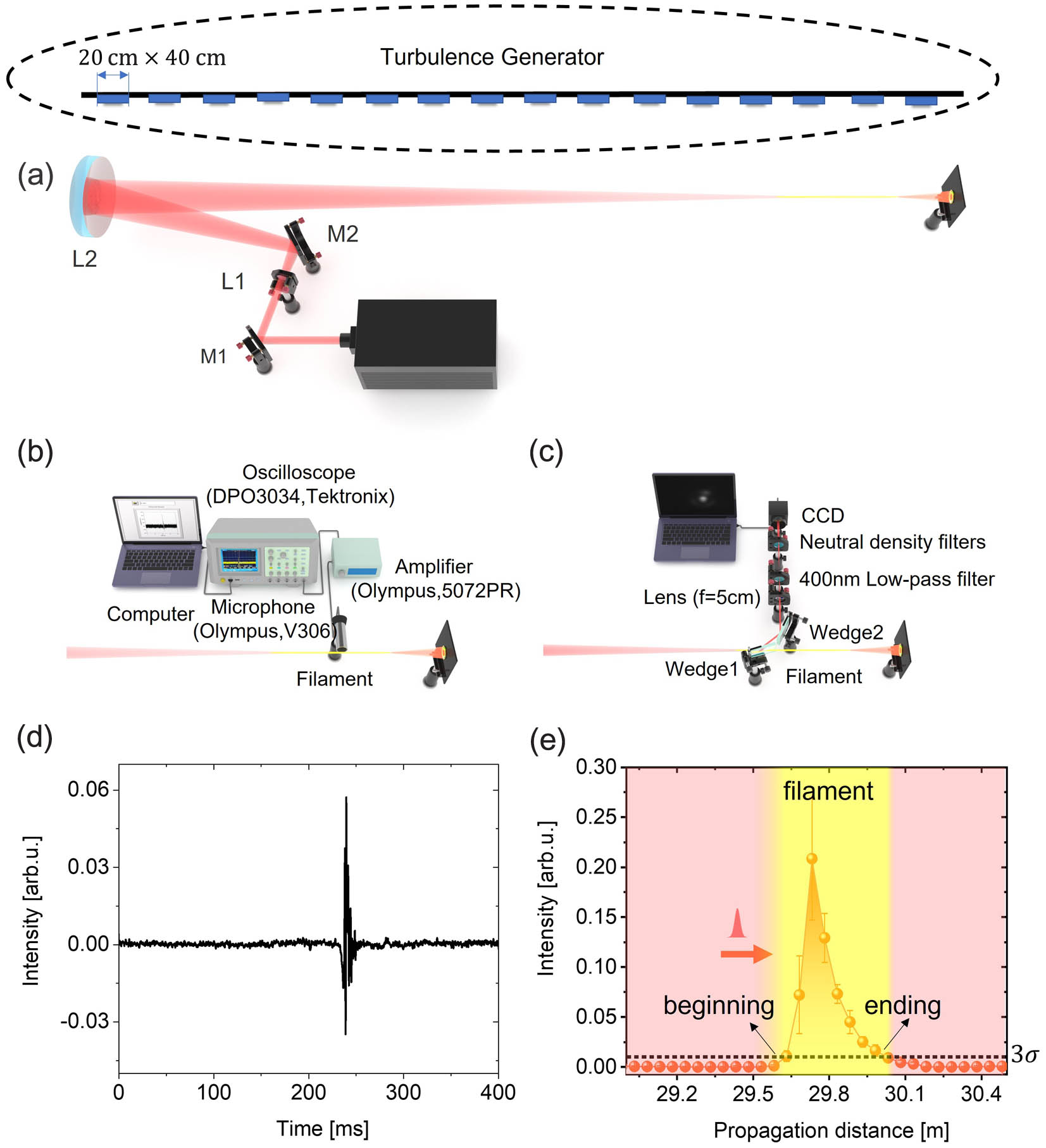
The effects of turbulence intensity and turbulence region on the distribution of femtosecond laser filaments are experimentally elaborated. Through the ultrasonic signals emitted by the filaments, it is observed that increasing turbulence intensity and an expanding turbulence active region cause an increase in the start position of the filament and a decrease in filament length, which can be well explained by theoretical calculation. It is also observed that the random perturbation of the air refractive index caused by atmospheric turbulence expands the spot size of the filament. Additionally, when the turbulence refractive index structure constant reaches , multiple filaments are formed. Furthermore, the standard deviation of the transverse displacement of filament is found to be proportional to the square root of the turbulent structure constant under the experimental turbulence parameters in this paper. These results contribute to the study of femtosecond laser propagation mechanisms in complex atmospheric turbulence conditions.
femtosecond laser filamentation turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Department of Electronic Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai, China
2 Nokia Bell Labs, Murray Hill, New Jersey, United States
3 Shanghai University, Key Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Optical Access Networks, Joint International Research Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Advanced Communication, Shanghai, China
4 Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, John Hopcroft Center for Computer Science, Shanghai, China
Mode-division multiplexing (MDM) technology enables high-bandwidth data transmission using orthogonal waveguide modes to construct parallel data streams. However, few demonstrations have been realized for generating and supporting high-order modes, mainly due to the intrinsic large material group-velocity dispersion (GVD), which make it challenging to selectively couple different-order spatial modes. We show the feasibility of on-chip GVD engineering by introducing a gradient-index metamaterial structure, which enables a robust and fully scalable MDM process. We demonstrate a record-high-order MDM device that supports TE0–TE15 modes simultaneously. 40-GBaud 16-ary quadrature amplitude modulation signals encoded on 16 mode channels contribute to a 2.162 Tbit / s net data rate, which is the highest data rate ever reported for an on-chip single-wavelength transmission. Our method can effectively expand the number of channels provided by MDM technology and promote the emerging research fields with great demand for parallelism, such as high-capacity optical interconnects, high-dimensional quantum communications, and large-scale neural networks.
integrated photonics metamaterial mode-division multiplexing subwavelength grating Advanced Photonics
2023, 5(5): 056008
1 南开大学软件学院,天津 300350
2 南开大学现代光学研究所,天津 300350
盐气溶胶是大气污染监测的重要对象。使用基于高功率超快激光的光丝诱导荧光光谱(FIFS)技术可以实现大气气溶胶的远距离快速定量分析,该技术有望成为下一代激光雷达的核心技术。用NaCl气溶胶模拟大气气溶胶污染物,针对自吸收效应导致光强与物质质量浓度偏离线性关系的问题,提出基于一维卷积神经网络的NaCl气溶胶质量浓度预测模型,并将其与多元线性回归模型、偏最小二乘回归模型、BP传播神经网络模型和定标曲线模型进行了对比实验。在各质量浓度(0.33~6.61 mg/m3)NaCl气溶胶全波段光谱数据集和特征波段光谱数据集上的实验结果表明:所提一维卷积神经网络模型在特征波段光谱数据集上的预测准确率为1,在泛化预测实验中的准确率为0.87,优于其在全波段光谱数据集上的结果,同时也优于其他模型。该模型对自吸收效应下的非线性定量分析具有良好的准确性和鲁棒性,为FIFS技术应用于大气气溶胶质量浓度预测分析提供了可靠的定量分析技术。
光谱学 光丝诱导荧光光谱 NaCl气溶胶定量分析 卷积神经网络
1 南开大学现代光学研究所,天津 300350
2 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室,天津 300350
3 天津市光电传感器与传感网络重点实验室,天津 300350
高强度的飞秒激光在非线性介质成丝过程中会产生一系列非线性效应,如强场电离、转动拉曼、高次谐波、激射等,这些非线性效应与强场下分子的复杂运动有关。研究强场作用下的分子动力学问题将有助于更好地理解飞秒激光成丝过程中非线性效应背后的物理机制。综述了近年来飞秒激光在空气中成丝时主要分子动力学特性的研究进展,包括分子准直、分子电离、电子-离子复合以及分子能级的粒子数布居。最后对强场与分子相互作用研究所面临的机遇以及挑战进行了展望。
非线性光学 飞秒激光成丝 强激光场 分子准直 强场电离 光丝诱导荧光
1 南开大学软件学院,天津 300350
2 南开大学现代光学研究所,天津 300350
大气污染对人类的生产生活有极大影响,气溶胶作为污染物的重要部分,不容忽视。提高对大气气溶胶浓度检测的精确性,尤其是低浓度气溶胶,具有十分重要的意义。本文基于光丝诱导荧光光谱技术,对NaCl气溶胶数据进行预处理,并结合偏最小二乘法建立预测模型,探索不同预处理方法对模型检测精度的影响。讨论如何科学合理地选择预处理方法,按照预处理方法效果分为散射校正、平滑去噪、基线校正3个方面,并提出波峰显著度算法。通过无预处理、单一预处理以及组合预处理进行最优预处理方法的选择,并分析其建模精度的影响。实验结果表明,应用多个预处理方法的组合,与无预处理相比,均方根误差降低至0.03,预测相对误差减少60%;与直接观察光谱信号选择预处理方法相比,根据光谱信噪比的提升及预测组分的建模效果可以更为准确地选择最佳预处理方法。该研究为开展低浓度大气污染物的分析研究提供了一定的参考。
大气光学与海洋光学 光丝诱导荧光光谱 光谱处理 低浓度氯化钠气溶胶检测 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(1): 0101001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
4 Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan
5 Peking University Yangtze Delta Institute of Optoelectronics, Nantong, 226010 JiangsuChina
6 Center for Emergent Functional Matter Science, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 30010, China
The THz generation efficiency and the plasma density generated by a filament in air have been found anti-correlated when pumped by two-color laser field. The plasma density near zero delay of two laser pulses has a minimum value, which is opposite to the trend of THz generation efficiency and contradicts common sense. The lower plasma density cannot be explained by the static tunneling model according to the conventional photocurrent model, but it might be attributed to the electron trapping by the excited states of nitrogen molecule. The present work also clarifies the dominant role of the drifting velocity accelerated by the two-color laser field during the THz pulse generation process. The results promote our understanding on the optimization of the THz generation efficiency by the two-color laser filamentation.
Ultrafast Science
2022, 2(1): 9853053
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 School of Physical Science and Technology, Tiangong University, Tianjin 300387, China
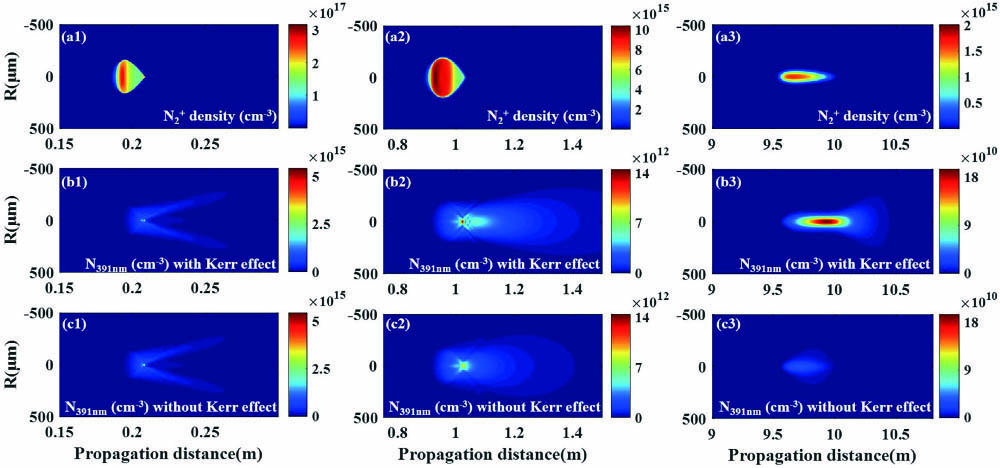
The spatial distribution of the forward-propagating amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) of nitrogen molecular ions during femtosecond laser filamentation in air is studied via numerical simulations. The results suggest that the divergence angle and signal intensity are extremely sensitive to the external focal length. Concurrently, we show that the optical Kerr effect plays a significant role in concentrating the directivity of ASE signals, particularly in cases of loose focusing. Furthermore, the simulations demonstrate that ASE signals are enhanced for a tight focus, although the corresponding filament length is shorter. The main physical mechanism underlying this process is the competition between the plasma defocusing and optical Kerr effects. The result is important for filamentation-based light detection and ranging applied to remote sensing.
air laser amplified spontaneous emission femtosecond laser filamentation Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(8): 081402
1 华北电力大学 环境科学与工程学院, 资源环境系统优化教育部重点实验室, 北京 102206
2 南开大学 现代光学研究所, 天津 300350
研究采用分子动力学模拟(Molecular dynamics simulation, MD)的方法, 以苯酚、α-萘酚和4-辛基酚为代表, 研究了酚类有机污染物(Phenolic Organic Pollutants, POPs)在氧化石墨烯(Graphene Oxide, GO)上单独和竞争吸附过程。通过自由能计算得到三种POPs在GO表面的吸附能分别为: 4-辛基酚(41.34 kJ/mol)>α-萘酚(33.23 kJ/mol)>苯酚(19.31 kJ/mol)。吸附过程中的主要作用力为POPs的疏水作用, 而分子团簇、范德华相互作用、静电相互作用以及氢键等在一定程度上增加了GO对POPs的吸附能力。在混合体系中, POPs之间存在明显的竞争吸附现象, 吸附过程包含了直接吸附和形成分子团簇的间接性吸附两个过程。本研究结果为含POPs水体的治理以及GO材料的设计和筛选提供了一定的理论依据。
酚类有机污染物 氧化石墨烯 竞争吸附 分子动力学模拟 phenolic organic pollutants graphene oxide competitive adsorption molecular dynamics simulation
南开大学现代光学研究所, 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室, 天津 300071
在大气污染物中有害气体成分众多,运用太赫兹、红外等振动光谱检测所得不同成分的吸收峰较难辨别。设计了一种根据所测光谱中可能包含的物质的理论光谱分析所测光谱中不同物质所占比重的算法。利用实验峰值与不同理论峰值的对应关系构建超定方程组,分别基于遗传算法和模拟退火算法进行求解,得到实验光谱中各物质理论光谱的贡献。为了验证所提算法的准确性,利用该算法对已知水团簇组成的水汽系统的实验光谱进行了分析,结果表明:所提算法能够得到不同成分的比重,具有较强的实用性。
光谱学 振动光谱 成分分析 超定方程组 遗传算法 模拟退火算法 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(9): 093001
近年来, 以有机无机杂化铅卤钙钛矿为吸光层的薄膜太阳能电池受到了广泛的关注, 不到十年时间其光电转换效率已经从3.8%提高到了23%, 这主要归因于有机铅卤钙钛矿材料光吸收系数高, 带隙合适并易于调控, 电子-空穴扩散长度长等优点。 2016年GrtzelL等人利用低气压快速去除薄膜前驱体溶剂的方法, 获得了高质量的甲脒和溴离子掺杂钙钛矿薄膜。 相比于其他传统的溶液制备方法, 这种方法能够很好的解决大面积均匀性的问题, 为高效率、 大面积钙钛矿太阳电池产业化提供了可能。 钙钛矿薄膜的成份、 结构及其光学性能对于太阳电池的器件性能起决定性作用, 因此在该制备技术下, 研究不同掺杂种类钙钛矿薄膜对光学性质的影响具有积极的意义。 利用真空闪蒸溶液技术制备了3种成分的钙钛矿薄膜, 利用扫描电镜、 X射线衍射, 吸收光谱和荧光光谱等表征手段对薄膜的形貌、 结构和光学性质进行了研究。 结果表明, 该技术可以用于制备均匀致密、 无针孔的高质量甲脒、 溴离子掺杂和氯离子掺杂的钙钛矿薄膜(成分分别为(FAPbI3)0.85(MAPbBr3)0.15, MA3PbI3和MAPb(IxCl1-x)3), 薄膜中晶粒的尺寸分别为500, 100和200 nm左右; 薄膜的形成过程为溶剂中的DMSO与钙钛矿配位, 并在真空闪蒸过程中快速形成相对稳定中间相, 经过加热后, 薄膜中的DMSO被去除并形成钙钛矿晶体, 结构为四方相; 甲脒、 溴离子和氯离子掺杂的薄膜对可见光有强烈的吸收作用, 薄膜吸收边均在750 nm左右; 薄膜的掺杂对带隙宽度没有明显影响, 3种成份的薄膜带隙宽度位于1.6 eV左右; 甲基胺碘化铅的荧光发射峰在765 nm, 甲脒和溴离子掺杂后发光峰位红移至774 nm, 氯离子掺杂后薄膜峰位处于761 nm, 有微弱的蓝移, 且强度出现下降。 这可能是晶粒尺寸和薄膜内部缺陷变化导致的。
真空闪蒸法 钙钛矿薄膜 光学特性 Vaccum-flash method Perovskite film Optical property





